Press
Genetic architecture may be key to using peacekeeping immune cells to treat autoimmunity or fight cancer
LA JOLLA—Regulatory T cells are specialized immune cells that suppress the immune response and prevent the body from attacking its own cells. Understanding how these cells work is key to determining how they might be manipulated to encourage the destruction of cancer cells or prevent autoimmunity. Cell behavior is influenced by chromatin architecture (the 3D shape of chromosomes) and which genes are accessible to proteins—like Foxp3, which promotes regulatory T cell development.
Salk Institute promotes five faculty members in genetics, structural biology, immunobiology, and neuroscience
LA JOLLA—Five Salk Institute faculty members have been promoted for their notable, innovative contributions to science. These faculty members have demonstrated leadership in their disciplines, pushing the boundaries of basic scientific research. Assistant Professors Sung Han, Dmitry Lyumkis, and Graham McVicker were promoted to associate professors, and Associate Professors Sreekanth Chalasani and Ye Zheng were promoted to professors. The promotions were based on Salk faculty and nonresident fellow recommendations and approved by Salk’s president and Board of Trustees on April 21, 2023.
Salk scientists receive $1.5 million from Sol Goldman Charitable Trust to research multiple sclerosis treatments
LA JOLLA—Salk Professor Ronald Evans and an interdisciplinary group of Institute researchers have been awarded a two-year, $1.5 million grant from the Sol Goldman Charitable Trust at the direction of cardiologist and Salk Trustee Benjamin Lewis. The award will fund a research project to explore connections between the gut, brain, and immune system in search of new therapies for patients with multiple sclerosis (MS).
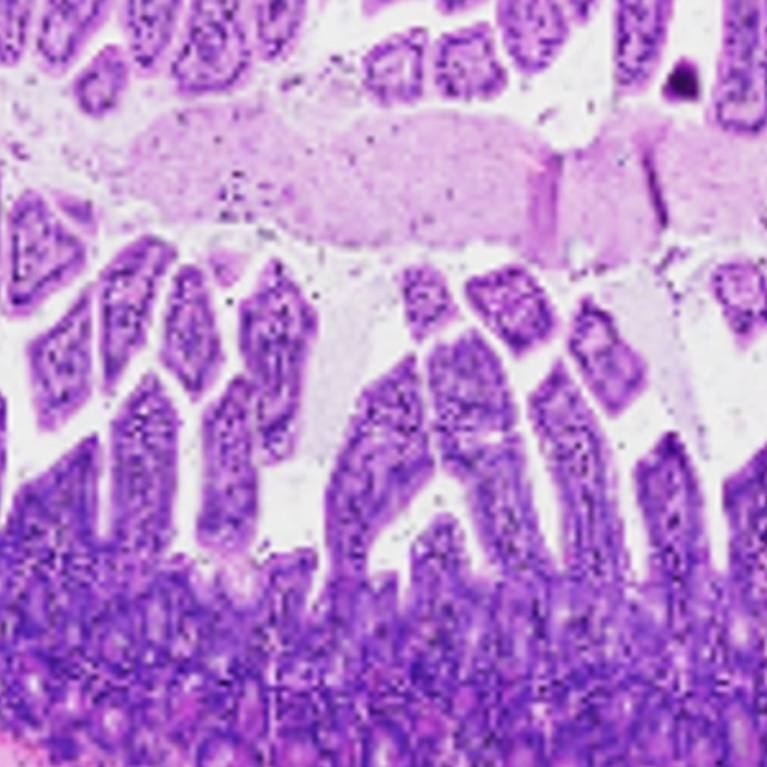
Salk scientists develop compound that reverses gut inflammation in mice
LA JOLLA—A drug developed by Salk Institute researchers acts like a master reset switch in the intestines. The compound, called FexD, has previously been found to lower cholesterol, burn fat, and ward off colorectal cancer in mice. Now, the team reports in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences on December 12, 2022, that FexD can also prevent and reverse intestinal inflammation in mouse models of inflammatory bowel disease.
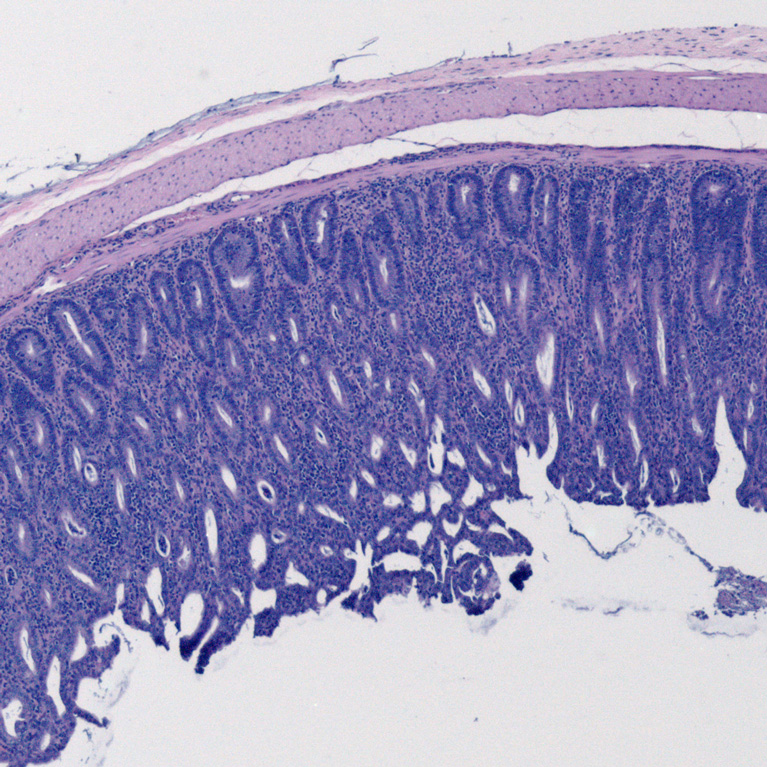
Hair-raising research: Salk scientists find surprising link between immune system, hair growth
LA JOLLA—Salk scientists have uncovered an unexpected molecular target of a common treatment for alopecia, a condition in which a person’s immune system attacks their own hair follicles, causing hair loss. The findings, published in Nature Immunology on June 23, 2022, describe how immune cells called regulatory T cells interact with skin cells using a hormone as a messenger to generate new hair follicles and hair growth.
How obesity can rewire the immune system and the response to immunotherapy—and how to change that
LA JOLLA—When mice with atopic dermatitis—a common type of allergic skin inflammation—are treated with drugs that target the immune system, their thickened, itchy skin generally heals quickly. But scientists have now discovered that the same treatment in obese mice makes their skin worse, instead. That is because obesity changes the molecular underpinnings of allergic inflammation, both in mice and humans.
Salk scientists discover genetic “dial” to turn immune function up and down to target cancer, autoimmune disease
LA JOLLA—The human immune system is a finely-tuned machine, balancing when to release a cellular army to deal with pathogens, with when to rein in that army, stopping an onslaught from attacking the body itself. Now, Salk researchers have discovered a way to control regulatory T cells, immune cells that act as a cease-fire signal, telling the immune system when to stand down.
New target for autoimmune disease could enable therapies with fewer side effects
LA JOLLA—Your immune system comes ready for battle against bacteria, viruses, fungi and even cancer. But in cases of autoimmune disease, the immune system’s superpowers turn it into a supervillain. Now, Salk Institute scientists have discovered a way to stop certain immune system cells from mistakenly attacking the body. Their findings, published the week of August 26, 2019, in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, suggest a new way to target Th17 helper T cells, a type of immune cell that produces interleukin 17, a molecule known to be at the root of autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis and psoriasis. Previous efforts targeting Th17 helper T cells have had limited success.
Immune cell policing offers insights into cancer, autoimmune disease
LA JOLLA—Regulatory T cells (Tregs) are the traffic cops of the immune system. They instruct other types of immune cells on when to stop and when to go. Learning how to direct the activity of Tregs has important implications for improving cancer immunotherapy as well as developing better treatments for autoimmune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes.
Salk promotes four leading scientists in the fields of neuroscience, circadian rhythms and immunology
LA JOLLA–Four Salk Institute faculty members have been promoted after the latest round of faculty reviews determined they are scientific leaders who have made original, innovative and notable contributions to biological research.
Blocking immune cell treats new type of age-related diabetes
LA JOLLA—Diabetes is often the result of obesity and poor diet choices, but for some older adults the disease might simply be a consequence of aging. New research has discovered that diabetes—or insulin resistance—in aged, lean mice has a different cellular cause than the diabetes that results from weight gain (type 2). And the findings point toward a possible cure for what the co-leading scientists, Ronald Evans and Ye Zheng, are now calling a new kind of diabetes (type 4).
Genetic signal prevents immune cells from turning against the body
LA JOLLA–When faced with pathogens, the immune system summons a swarm of cells made up of soldiers and peacekeepers. The peacekeeping cells tell the soldier cells to halt fighting when invaders are cleared. Without this cease-fire signal, the soldiers, known as killer T cells, continue their frenzied attack and turn on the body, causing inflammation and autoimmune disorders such as allergies, asthma, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes.
Salk scientist named 2010 Rita Allen Scholar
LA JOLLA, CA–Dr. Ye Zheng, an assistant professor in the Nomis Laboratories for Immunobiology and Microbial Pathogenesis at the Salk Institute for Biological Studies, has been named a 2010 Rita Allen Scholar, the Rita Allen Foundation announced today. He will receive $500,000 over a five-year period to study how regulatory T cells prevent the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissue and causing autoimmune disease.